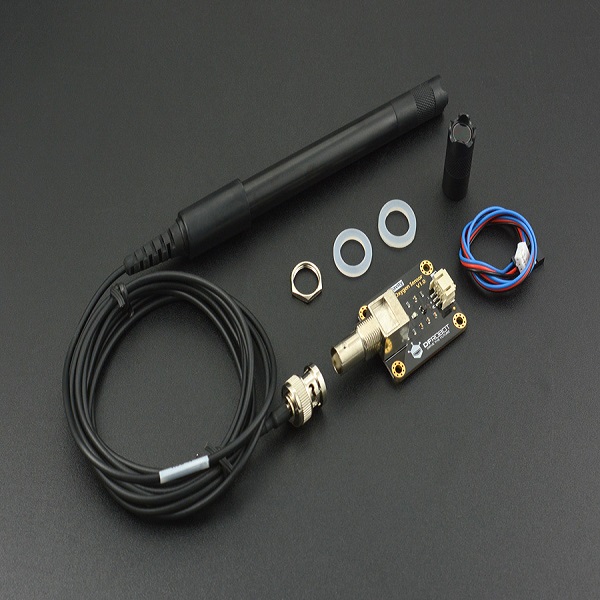
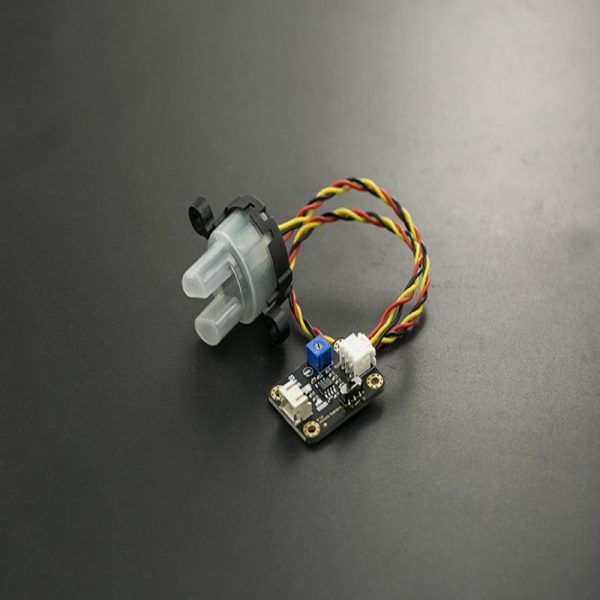
Gravity: Analog Dissolved Oxygen Sensor kit is compatible with Arduino microcontrollers. This product is used to measure the dissolved oxygen in water, to reflect the water quality. It is widely applied in many water quality applications, such as aquaculture, environment monitoring, natural science and so on.
The probe is a galvanic probe, no need of polarization time, and stay available at any time. The filling solution and membrane cap is replaceable, leading to the low maintenance cost. The signal converter board is plug and play, and has the good compatibility. It can be easily integrated to any control or detecting system.
Gravity: Analog Dissolved Oxygen Sensor is used to measure the dissolved oxygen in water, to reflect the water quality. This sensor kit helps you quickly to build your own dissolved oxygen detector.

SPECIFICATIONS
Dissolved Oxygen Probe
- Type: Galvanic Probe
- Detection Range: 0~20mg/L
- Response Time: Up to 98% full response, within 90 seconds (25℃)
- Pressure Range: 0~50PSI
- Electrode Service Life: 1 year (normal use)
- Maintenance Period: Membrane Cap Replacement Period: 1~2 months (in muddy water); 4~5 months (in clean water) Filling Solution Replacement Period: Once every month
- Cable Length: 2 meters
- Probe Connector: BNC
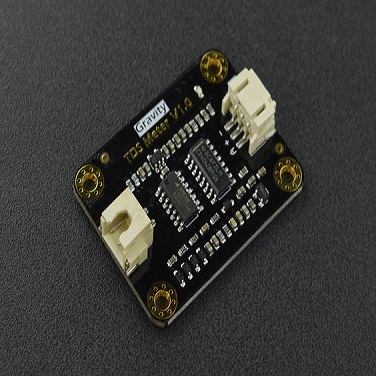
Signal Converter Board
- Operating Voltage: 3.3~5.5V
- Output Signal: 0~3.0V
- Cable Connector: BNC
- Signal Connector: Gravity Analog Interface (PH2.0-3P)
- Dimension: 42mm * 32mm
Dissolved oxygen refers to the level of free, non-compound oxygen present in water or other liquids. It is an important parameter in assessing water quality because of its influence on the organisms living within a body of water. In limnology (the study of lakes), dissolved oxygen is an essential factor second only to water itself ¹. A dissolved oxygen level that is too high or too low can harm aquatic life and affect water quality.
Non-compound oxygen, or free oxygen (O2), is oxygen that is not bonded to any other element. Dissolved oxygen is the presence of these free O2 molecules within water.The bonded oxygen molecule in water (H2O) is in a compound and does not count toward dissolved oxygen levels. One can imagine that free oxygen molecules dissolve in water much the way salt or sugar does when it is stirred
Dissolved oxygen is necessary to many forms of life including fish, invertebrates, bacteria and plants. These organisms use oxygen in respiration, similar to organisms on land. Fish and crustaceans obtain oxygen for respiration through their gills, while plant life and phytoplankton require dissolved oxygen for respiration when there is no light for photosynthesis 4. The amount of dissolved oxygen needed varies from creature to creature. Bottom feeders, crabs, oysters and worms need minimal amounts of oxygen (1-6 mg/L), while shallow water fish need higher levels (4-15 mg/L)⁵.
Microbes
Microbes such as bacteria and fungi also require dissolved oxygen. These organisms use DO to decompose organic material at the bottom of a body of water. Microbial decomposition is an important contributor to nutrient recycling. However, if there is an excess of decaying organic material (from dying algae and other organisms), in a body of water with infrequent or no turnover (also known as stratification), the oxygen at lower water levels will get used up quicker
Dissolved oxygen is usually reported in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or as a percent of air saturation. However, some studies will report DO in parts per million (ppm) or in micromoles (umol). 1 mg/L is equal to 1 ppm. The relationship between mg/L and % air saturation has been discussed above, and varies with temperature, pressure and salinity of the water. One micromole of oxygen is equal to 0.022391 milligrams, and this unit is commonly used in oceanic studies ⁴⁷. Thus 100 umol/L O2 is equal to 2.2 mg/L O2.


 Botzees
Botzees Keyestudio
Keyestudio Fischertechnik
Fischertechnik